3D Modeling is one of the most transformative digital design technologies of the modern era. It is the process of creating a virtual object, environment, or character in three dimensions using specialized software. Unlike traditional illustration or photography, modeling in 3D allows designers to build an object that can be viewed from any angle, textured with realistic surfaces, animated, or turned into a physical prototype.

Industries embracing digital modeling include:
- Architecture
- Gaming & Animation
- Film/VFX
- Product Manufacturing
- Medical & Scientific Visualization
- AR/VR Experiences
- Advertising & Marketing
Whether you’re designing a skyscraper, creating a game character, or developing a digital prototype for a new invention, modeling in 3D provides unmatched accuracy and creativity.
Table of Contents
2. What Is 3D Modeling? (Core Definition + Examples)
Modeling in 3D is the digital process of creating an object or scene within a three-dimensional space using vertices, edges, and polygons. These components form detailed models that can be rendered into photorealistic images, animated for video, or exported for production.
Examples of 3D Models:
- Architectural buildings
- Product prototypes
- Mechanical parts
- Animated characters
- Game environments
- 3D NFTs
- Medical anatomy models
- Virtual sets for filmmaking
Learn more about 3D graphics concepts:
🔗 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3D_modeling
3. Benefits of 3D Modeling Across Industries
Modeling in 3D is not just a creative art — it’s a powerful business tool.
Major advantages:
- Saves time & money by visualizing concepts early
- Improves communication between teams and clients
- Allows instant revisions & adjustments
- Enhances marketing with realistic visuals
- Enables physical prototypes through 3D printing
- Boosts product development speed
- Optimizes manufacturing accuracy
In industries like architecture and engineering, modeling in 3D eliminates guesswork. In entertainment and gaming, it enhances storytelling and immersive experiences.
4. Types of 3D Modeling (Beginner to Advanced)
Digital modeling is not one-size-fits-all. Different techniques are used depending on the project’s needs.
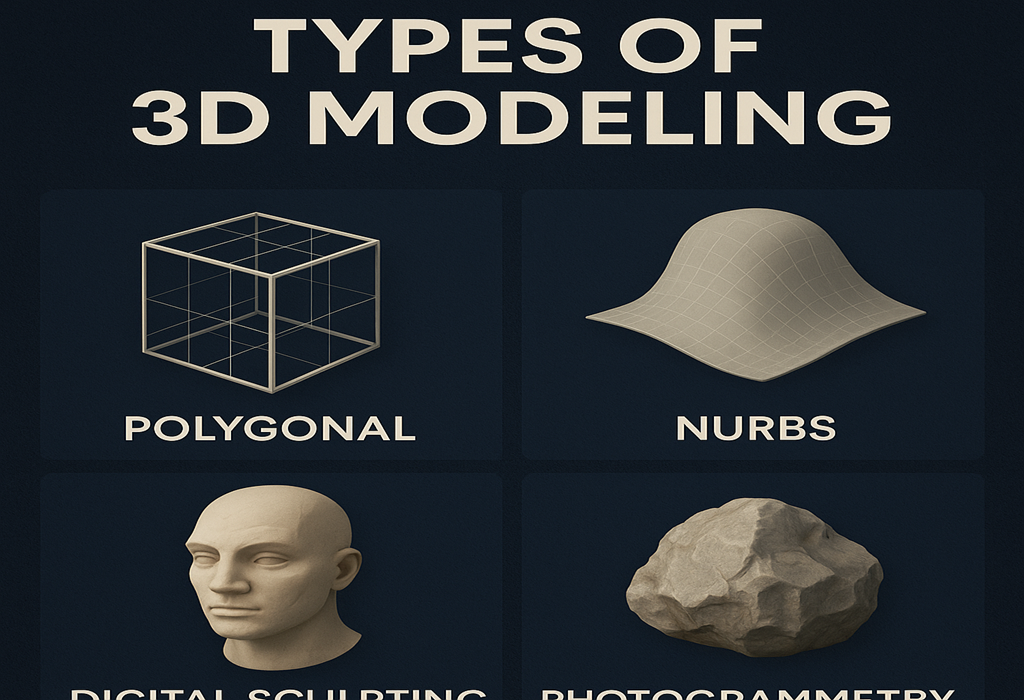
1. Polygonal Modeling
Using vertices and polygons — perfect for games and animation.
2. NURBS Modeling
Mathematical curves for smooth, precise surfaces — ideal for automotive and industrial design.
3. Digital Sculpting
Clay-like sculpting for highly detailed characters and organic shapes.
4. CAD Modeling
Engineering-accurate models used for manufacturing, mechanical parts, and product prototyping.
5. Procedural Modeling
Automated creation using algorithms and node-based systems.
6. Photogrammetry
Creating models from photos using computational reconstruction.
7. Kitbashing
Building models quickly using pre-made assets.
5. 3D Modeling Techniques Explained
Subdivision Modeling
Smooth, rounded surfaces controlled by base meshes.
Box Modeling
Starting from a cube and refining details — beginner-friendly.
Edge Loop & Topology Modeling
Critical for animation-ready models.
Retopology
Rebuilds geometry for performance and clean topology.
3D Sculpting & Surface Detailing
Used for high-poly creatures, characters, and organic forms.
6. 3D Modeling Workflow: From Concept to Final Render
A professional studio typically follows these steps:
1. Concept & Reference Gathering
Sketches, mood boards, blueprints.
2. Blocking / Base Mesh
Basic shapes to define form.
3. High-Poly / Sculpt
Add details and surface definition.
4. Retopology (if needed)
Clean topology for performance.
5. UV Unwrapping
Flattening surfaces so textures align perfectly.
6. Texturing & Material Creation
Colors, surface imperfections, patterns.
7. Lighting & Rendering
Creating photorealistic images or animations.
8. Final delivery
Render files, AR-ready assets, game engine files, etc.
7. Popular 3D Modeling Software (Free & Paid)

Free Tools
- Blender — Open-source powerhouse
- SketchUp Free — Great for beginners
Paid Tools
- Autodesk Maya — Film & animation industry standard
- Autodesk 3ds Max — Architecture, engineering, games
- ZBrush — Best for sculpting
- Cinema 4D — Motion graphics focus
- SolidWorks / Fusion 360 — CAD & manufacturing
- Rhinoceros 3D — Architecture & industrial design
Outbound authority:
🔗 https://www.autodesk.com
8. 3D Modeling for Architecture & Interior Design
Modeling in 3D revolutionized architecture. Clients no longer imagine — they experience the design.
Architectural designers use 3D modeling to:
- Present buildings realistically
- Test lighting & material choices
- Create virtual walkthroughs
- Improve construction planning
- Reduce project costs
Interior designers can showcase:
- Layouts
- Furniture
- Color schemes
- Materials & textures
- Lighting simulation
Software used: SketchUp, Revit, 3ds Max, Rhinoceros, Blender.
9. 3D Modeling for Product Design & Manufacturing
Manufacturers rely heavily on CAD modeling.
Why:
- Perfect mechanical accuracy
- Simulate functionality
- Reduce production errors
- Prepare for 3D printing
- Speed up prototyping cycles
Examples of CAD product models:
- Electronics housings
- Automotive parts
- Consumer goods
- Tools & machinery
- Packaging designs
Digital modeling shortens development time by 50–70%.
10. 3D Modeling for Animation, Games & Characters
This is one of the most creative uses of modeling in 3D.
Character modeling includes:
- Anatomy
- Facial topology
- Expression sculpting
- Clothing simulations
Environment modeling includes:
- Landscapes
- Cities
- Fantasy worlds
- Levels for games
Game engines that use 3D models:
🔗 https://www.unrealengine.com
🔗 https://unity.com
11. Texturing, UV Mapping & Photorealistic Rendering
A modeling in 3D is only half the story — texturing makes it feel real.
Techniques include:
- UV Unwrapping
- PBR workflow (Physically Based Rendering)
- Material node systems
- Baking maps: AO, Normal, Cavity, Roughness
- HDRI lighting
- Ray-tracing rendering
Render engines:
- Cycles
- Arnold
- V-Ray
- Redshift
- Octane
12. Low-Poly vs High-Poly Modeling
Low-Poly
Used for games, AR/VR, real-time experiences.
Fast to render, optimized for performance.
High-Poly
Used for cinematic shots, product rendering, marketing.
Extremely detailed.
13. Rigging, Sculpting & Animation-Ready Models
Animation-ready models require:
- Clean topology
- Proper edge loops
- Weight painting
- Skeleton systems
- Blendshapes for facial animation
Rigging allows characters to move naturally.
14. Optimized 3D Assets for AR, VR & Game Engines
To run smoothly in real-time engines:
- Reduce polygon count
- Bake high-poly details into maps
- Compress textures
- Organize UVs
- Use LODs (Levels of Detail)
Used in:
- Virtual stores
- AR product previews
- VR training simulations
- Metaverse experiences
15. Hiring Professional 3D Modelers
Hiring a skilled 3D artist can save time, increase quality, and help a project succeed.
Reasons to hire a professional:
- Better topology & clean modeling
- Accurate textures & materials
- Faster turnaround
- Professional rendering
- Optimized files for your platform
➡️ If you want to hire expert modeling in 3D for professional projects, you may explore recommended service providers here:
🔗 https://topratedaffi.com/recommends/3d-modeling/
16. Benefits of Outsourcing 3D Modeling Services
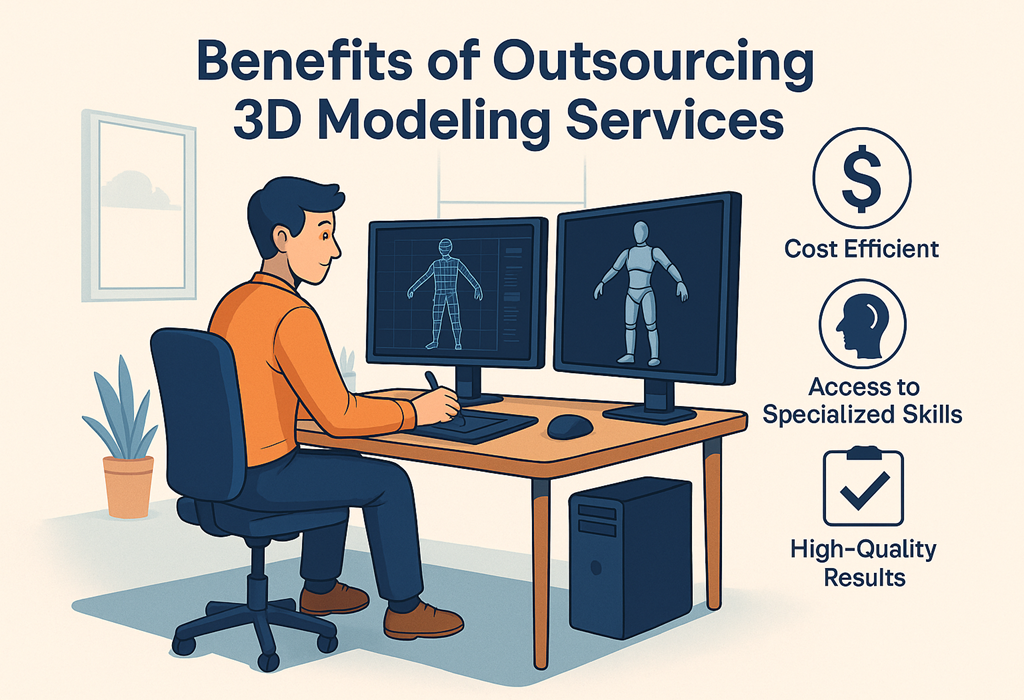
1. Cost Efficient
Hiring an in-house 3D artist is expensive. Outsourcing saves money.
2. Faster Project Completion
Studios work in teams.
3. Access to Specialized Skills
Hard-surface modeling, character sculpting, CAD modeling — different artists excel in different areas.
4. Scale When Needed
Start small and expand as your project grows.
5. High-Quality Results
Experienced modelers deliver consistent, accurate, detailed work.
17. Signs You Need a Professional 3D Modeling Studio
- You need photorealistic renderings
- Your model must be animation-ready
- You lack time to learn software
- Your project requires CAD-level precision
- You want assets optimized for game engines
- You need a complete environment built from scratch
18. Why 3D Modeling Is Essential in 2025
The demand for modeling in 3D is rising due to:
- AI-assisted modeling tools
- AR/VR adoption
- Real-time 3D becoming standard
- 3D product visualization in eCommerce
- Digital twins for industrial applications
- Advancements in gaming graphics
- 3D printing & rapid prototyping
Companies that embrace 3D gain a competitive advantage.
19. Conclusion: Bring Your Idea to Life
Digital Modeling has changed how the world creates products, films, buildings, and digital experiences. Whether you’re an entrepreneur, architect, game developer, engineer, or marketer, modeling in 3D empowers you to visualize, refine, and improve ideas with precision and beauty.
If you need high-quality, professional digital models — characters, products, interiors, animations, or environments — working with an experienced 3D modeler ensures your project is completed accurately and efficiently.
👉 Explore top-rated digital modeling services here (affiliate-support link):
🔗 https://topratedaffi.com/recommends/3d-modeling/
20. Author Bio
Author: An Independent 3D Design & Digital Technology Enthusiast
As an affiliate marketer and content creator specializing in 3D design, digital tools, and creative software, I share resources that help designers, entrepreneurs, and businesses bring ideas to life. I may earn a small commission from recommended services — at no extra cost to you. My mission is to provide value-driven guidance backed by real industry knowledge and ethical affiliate practices.
